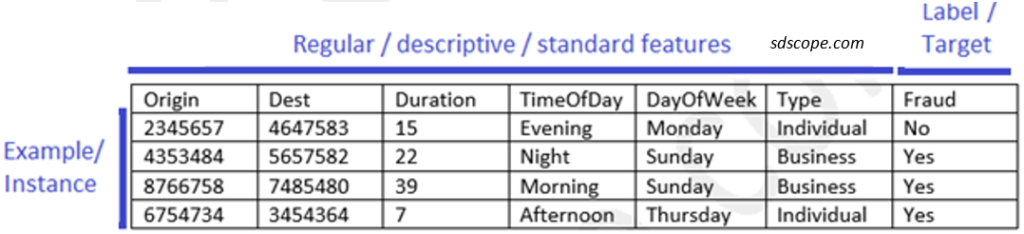
A dataset is a simple, flat table containing historical data of the scenario for which predictions are to be made. Each row, referred to as an example or an instance, contains data for a single observation about a problem. Each column, referred to as an attribute, a variable or a dimension contains a feature of the observation.
In supervised machine learning columns are divided into a set of descriptive features also called standard features, regular features or simply features, and a single target feature also called a label or an outcome. The dataset for an unsupervised learning task does not have a label, i.e., the dataset is “unlabeled“.
The features that come directly from raw data sources, e.g., Origin, Dest, and DayOfWeek in the above diagram are referred to as raw features while those that do not exist in any raw data source or are created from one or more features in a data source, e.g., Duration (if calculated from “call start time” and “call end time”) and TimeOfDay (if derived from the actual time on the timestamp) are referred to as derived features.




